How to Properly Use a High Pressure Homogenizer?
How to Properly Use a High Pressure Homogenizer?
High-pressure homogenizers are indispensable tools across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and biotechnology. They perform a range of tasks, from cell disruption to particle size reduction. To ensure both efficient and safe operation, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of how to properly use a high-pressure homogenizer. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide, focusing on the essential steps for effective utilization.1. Understanding the Basics
To begin, let's delve deeper into the core components and functionalities of a high-pressure homogenizer. A typical high-pressure homogenizer comprises a pump, a homogenization chamber, and various valves and connectors. The pump serves as the workhorse, generating the immense pressure required for the homogenization process. The homogenization chamber, often a microfluidic interaction chamber, is the stage where this process unfolds.2. Preparation: Ensuring a Smooth Start
The journey to proper high-pressure homogenizer use commences with meticulous preparation:Connector Alignment: Verify that all connectors and hoses are correctly positioned. Adhere strictly to the rated pressure class for connectors and hoses. When dealing with electric wiring, ensure it aligns with the equipment's rated voltage and current specifications.
Moderate Tightness: Thread fittings should not be excessively tight or too loose. Maintain a moderate level of tightness for optimal performance.
Proper Pipe Fittings: All pipe fittings must be securely connected to the outlet and inlet, ensuring they stay within the load capacity of the High Pressure homogenizer.
Medium Compatibility: The selected medium must be compatible with 316L stainless steel. In cases of uncertainty regarding the medium's properties, consult the manufacturer for detailed guidance. Commonly used mediums include distilled water, soluble oil (water-in-oil emulsion), petroleum, alcohol, diester, acetone, silicone oil, lipids, surfactants, other organic solvents, and strong acids and bases.
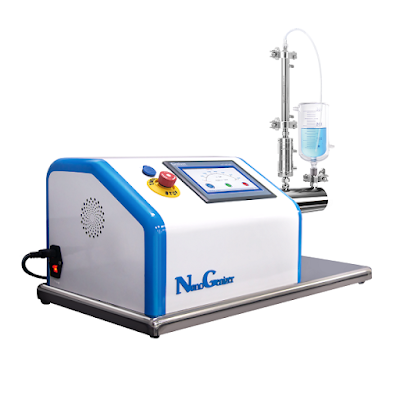

NanoGenizer High Pressure Homogenizer
Titanium Cylinder: For specific applications, a titanium cylinder may be necessary. It's essential to understand that improper medium use leading to significant corrosion damage may not be covered by the equipment's warranty.
3. Installation: Laying the Foundation for Success
Proper installation sets the stage for effective homogenization:
Homogenizer Placement: Given its weight, place the equipment on a stable platform. The equipment's non-slip foot-pads obviate the need for additional fixing methods. Additionally, allocate sufficient space for safe and convenient operation.
Homogenizer Assembly: While most components come pre-assembled, some peripherals with different joint pipes may need to be assembled by the operator. Refer to the component detailed parts drawing in the Components List for precise assembly instructions.
In conclusion
High-pressure homogenizers are formidable tools that demand meticulous operation and maintenance. By adhering to these comprehensive guidelines and comprehending the equipment's capabilities, you can consistently achieve efficient and reliable results in your homogenization processes. With the right knowledge and care, these powerful machines can unlock new possibilities across various industries.Related Articles
Using NanoGenizer High Pressure Homogenizers for Nanomaterials.
Liposome Extruders: Functions, Mechanisms, and Types
Liposome Processing: High Pressure Homogenizer vs Liposome Extruder
High Pressure Homogenization vs Sonication: Which is Better for Your Liquid Formulation?
How to choose a High Pressure Homogenizer?
Benefits of Ultra High Pressure Homogenizer
Microfluidic High Pressure Homogenizer vs Conventional High Pressure Homogenizer, How to Choose?

Comments
Post a Comment