High Pressure Homogenizer VS Microfluidizer, How to Choose?
When it comes to particle size reduction, emulsion formation, and cell disruption, two commonly used equipment options are high-pressure homogenizers (conventional valve homogenizers)and microfluidizers (cutting-edge high pressure microfluidic homogenizers). These technologies excel at achieving consistent particle size distribution and enhancing product quality across various industries. In this comparison, we will explore the differences between high-pressure homogenizers and microfluidizers, highlighting their unique features, advantages, and important considerations. By the end, you will have the knowledge needed to make an informed decision when selecting the appropriate equipment.
High-Pressure
Homogenizers (conventional valve homogenizers):
High-pressure homogenizers are robust
machines that utilize high pressure and mechanical forces to process materials.
They consist of a piston-driven homogenizing valve, which propels the sample
through a narrow gap, resulting in intense turbulence and shear forces. This
process effectively breaks down particles, emulsifies liquids, and disrupts
cells.
Advantages
of High-Pressure Homogenizers (conventional valve homogenizers):
Versatility: High-pressure homogenizers can
handle a wide range of sample volumes, making them suitable for both small and
large-scale production. This makes them well-suited for industrial-scale
production where a significant amount of material needs to be processed.
Additionally, they can process viscous liquids, suspensions, and emulsions with
ease.
Microfluidizer
Homogenizers (high-pressure microfluidic homogenizers):
Microfluidizers, on the other hand, utilize microfluidic
diamond interaction chambers to achieve a uniform distribution of
nanoparticles with pharmaceutical-grade quality. These chambers are specially
designed with a fixed geometry that facilitates mechanical forces such as high
shearing, high-frequency oscillation, cavitation, convective impact, and
thermal effects. These combined effects induce changes in the physical,
chemical, and particle structure of the materials, resulting in a more uniform
and smaller nanoparticle size, ultimately achieving a superior homogenization
effect. Microfluidizers find wide applications in the pharmaceutical, biotech, cosmetics,
chemical, and diverse industries.
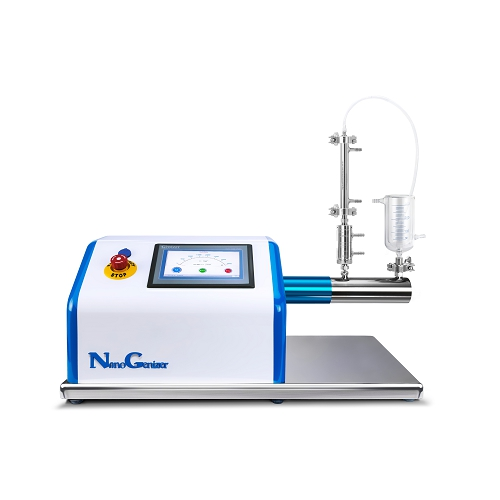 |
| Genzier High Pressure Microfludizer Homogenizers |
Genizer LLC is one of two companies in
the world that supplies high pressure microfluidic homogenizers (Microfluidizers)
equipped with original microfluidic diamond interaction chambers. In recent
years, Genizer’s microfluidic diamond interaction chambers have been equipped
by more and more homogenizer manufacturer
 |
| Genizer Microfluidic Interaction Chambers |
 |
| Inner structure of Genizer Microfluidic Interaction Chambers |
Advantages
of Microfluidizers:
Enhanced
Efficiency: Microfluidizers are highly effective in
achieving significant particle size reduction and superior homogenization
efficiency. The precisely controlled fluid dynamics within the microchannels of
the interaction chamber enable accurate manipulation of shear forces, resulting
in precise and controlled particle size reduction and uniform particle
distribution.
Scalability:
Microfluidizers
offer seamless scalability, allowing for the smooth transition of research
findings into large-scale production. This enables efficient technology
transfer from laboratory-scale experimentation to industrial manufacturing
processes.
Scalability:
Microfluidizers
offer seamless scalability, facilitating the seamless transfer of research
findings into large-scale production. This enables efficient technology
transfer from laboratory-scale experimentation to industrial manufacturing
processes.
Reduced Heat
Generation: Microfluidizers
operate at lower pressures compared to high-pressure homogenizers, resulting in
reduced heat generation during the process. This makes them suitable for
heat-sensitive materials.
Choosing between a high-pressure homogenizer and a microfluidizer homogenizer depends on several factors. Consider the following key points to make an informed decision.
Application
Requirements: Evaluate your specific application needs,
including particle size requirements, sample viscosity, and desired throughput.
Due to their advantages in price and resistance to clogging, high-pressure
homogenizers are suitable for applications such as cell disruption,
high-viscosity chemical materials, dairy beverages, inkjet pigments, and
particle size reduction where high purity is not required. While Microfluidizer
Homogenizers are commonly used in the field of nanoemulsion dispersion and
high-value applications such as cosmetics, nano new materials, food, graphene,
and pharmaceuticals (e.g., paclitaxel liposomes, docetaxel, propofol).
Sample
Characteristics: Take into account the nature of your sample,
including its heat sensitivity, fragility, and susceptibility to clogging.
High-pressure homogenizers may be more suitable for robust samples, while
microfluidizers are advantageous for heat-sensitive or delicate materials.
Production Scale: Assess your current and future production volumes and choose the technology that aligns with your production requirements. High-pressure homogenizers are generally more suitable for larger-scale production and applications that require higher throughput, while microfluidizers are better suited for smaller-scale production and applications that require more precise control over particle size and distribution.
Budget Considerations: Take into account your budget and compare the costs associated with both equipment options, including initial purchase costs, maintenance expenses, and operational costs. Also, consider the long-term return on investment (ROI). The cost of a high-pressure homogenizer or microfluidizer may vary based on the specific models and features. Generally, high-pressure homogenizers have a lower price compared to microfluidizers, especially for large-scale production. However, microfluidizers can offer cost savings through reduced energy consumption, smaller size, and minimized material waste due to their ability to achieve more precise particle size reduction.
Expertise and Support: Evaluate the availability of technical expertise and after-sales support for the chosen equipment. Consider factors such as training, maintenance, and troubleshooting assistance provided by manufacturers or suppliers.
Future Needs
and Flexibility: Anticipate any future requirements or
potential changes in your production process. Choose a technology that allows
for flexibility and adaptability to accommodate evolving needs.
In conclusion, when deciding between a
high-pressure homogenizer and a microfluidizer homogenizer, several factors
should be considered. High-pressure homogenizers are more suitable for
industries with larger flow requirements and lower homogenization standards,
such as the food and beverage, chemical, and generic pharmaceutical industries.
On the other hand, microfluidizer homogenizers, such as NanoGenizer, are ideal
for applications that demand higher performance and precision, such as the
pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and cosmetics industries, as well as research
laboratories and institutes that prioritize research quality. While
high-pressure homogenizers offer a cost-effective solution, microfluidizer
homogenizers provide enhanced efficiency and ease of use. Therefore, the choice
should be based on specific application requirements and the desired level of homogenization
quality.


Comments
Post a Comment